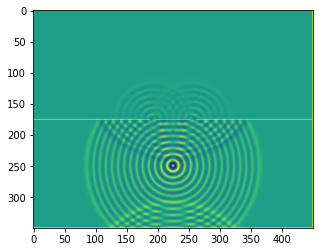
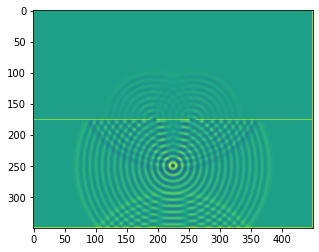
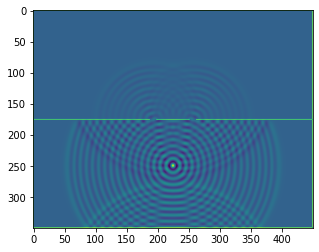
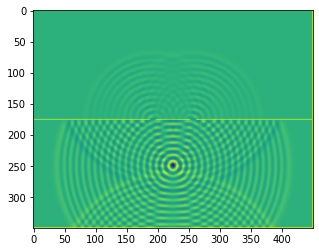
A double slit experiment#
Author Audun Skau Hansen ✉️
The Hylleraas Centre for Quantum Molecular Sciences, 2022
Richard Feynman once famously claimed that exerything in quantum mechanics can be understood in light of the double slit experiment. In his own words, it “contains the only mystery” of quantum physics.
If this is true, it is (perhaps) good news. It means that all we have to do to master quantum physics is to properly simulate the double slit experiment, and derive all insight from our results. So let’s do just that. And maybe we’ll steer clear of profound philosophical conundrums along the way.
A classical wave in a box#
In the following simulations we shall use the wavebox extension of BubbleBox:
import bubblebox as bb
from bubblebox.wavebox import boundaries_edge
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
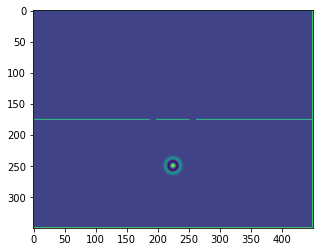
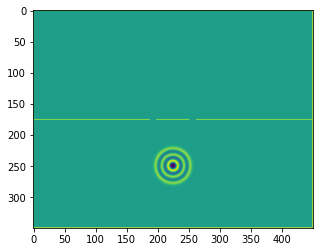
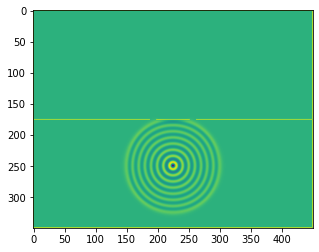
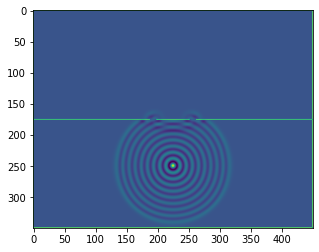
b = bb.wavebox(resolution = (350,450), size = (3.5,4.5))
# set initial state
#b.u = np.exp(-500*((b.x[0][:, None] - 1.5)**2 + b.x[1][None,:]**2))
def boundaries_single_slit(resolution, slitwidth = 5):
bo = np.zeros(resolution, dtype = bool)
bo[:, 0] = True
bo[:, -1] = True
bo[int(resolution[0]/2), :int(resolution[1]/2)-slitwidth] = True
bo[int(resolution[0]/2), int(resolution[1]/2)+slitwidth:] = True
bo[0,:] = True
bo[-1,:] = True
return bo
def source(t):
return 20*np.exp(-500*((b.x[0][:, None] - 1.5)**2 + b.x[1][None,:]**2))*np.sin(25*t)
b.source = source
# set boundary conditions
b.set_neumann_boundary_conditions(boundaries_single_slit(b.resolution))
interference_pattern = np.zeros(b.resolution[1], dtype = float)
for i in range(20):
for j in range(80):
b.advance()
interference_pattern += b.u[1]**2
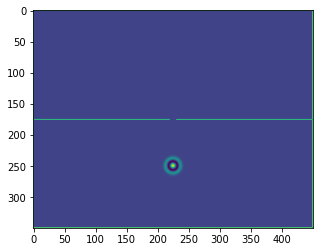
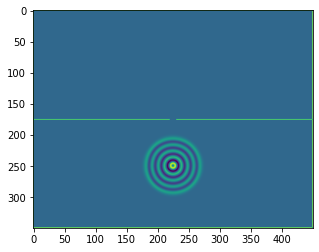
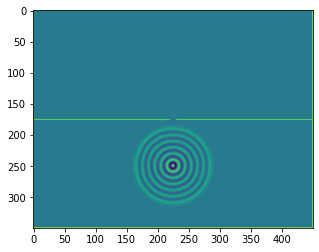
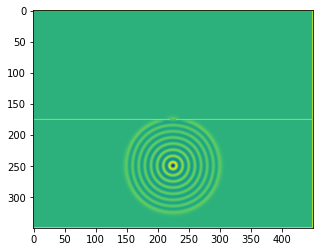
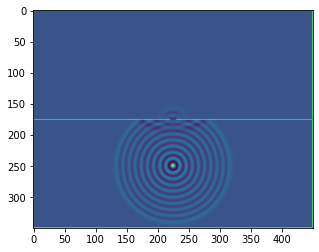
plt.figure()
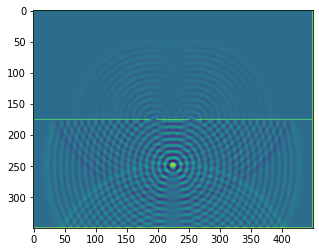
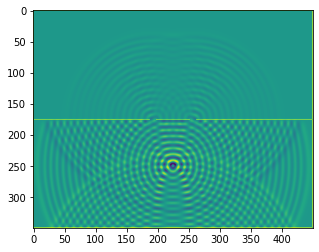
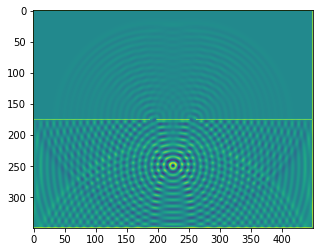
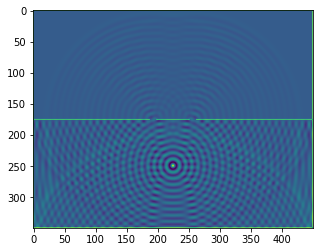
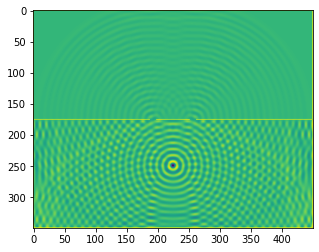
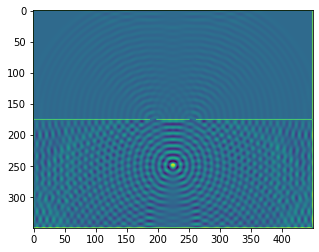
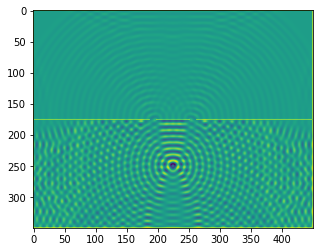
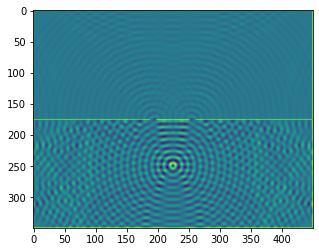
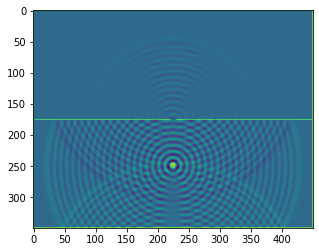
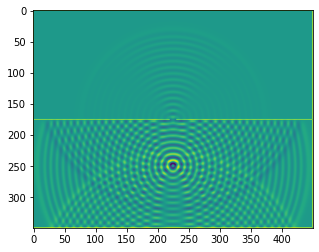
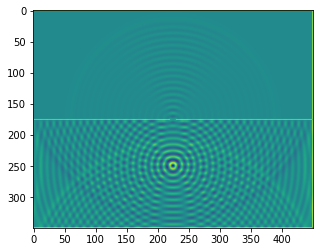
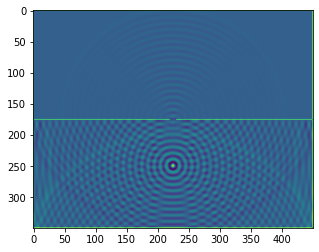
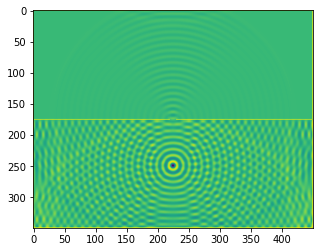
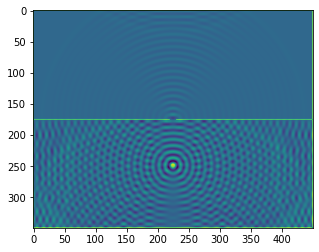
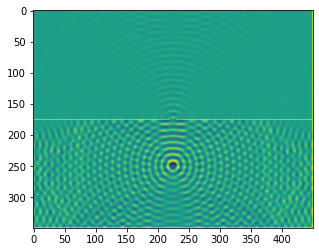
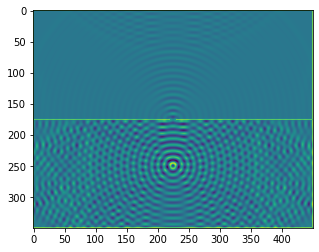
plt.imshow(b.representation())
plt.show()
plt.figure()
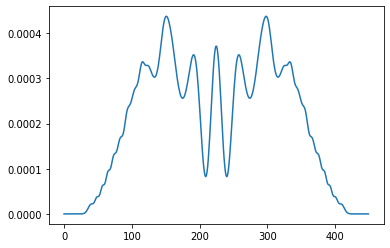
plt.plot(interference_pattern)
plt.show()

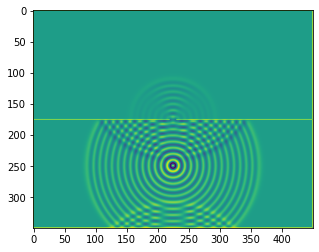
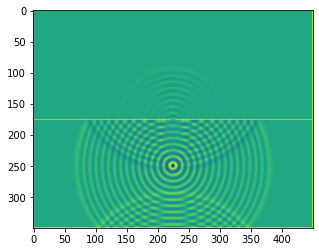
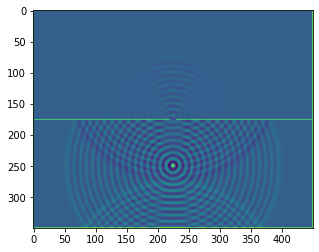
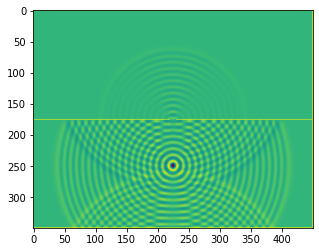
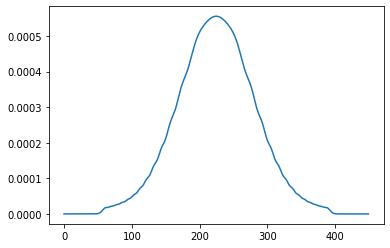
def boundaries_double_slit(resolution, slitwidth = 5, slit_separation = 32):
bo = np.zeros(resolution, dtype = bool)
bo[:, 0] = True
bo[:, -1] = True
bo[int(resolution[0]/2), :]=True
bo[int(resolution[0]/2), int(resolution[1]/2)-slit_separation-slitwidth:int(resolution[1]/2)-slit_separation+slitwidth] = False
bo[int(resolution[0]/2), int(resolution[1]/2)+slit_separation-slitwidth:int(resolution[1]/2)+slit_separation+slitwidth] = False
bo[0,:] = True
bo[-1,:] = True
return bo
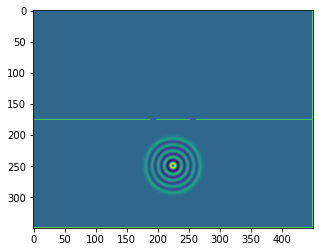
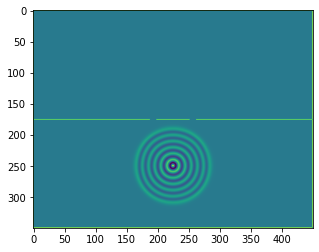
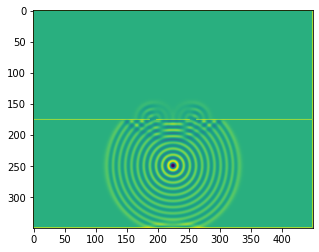
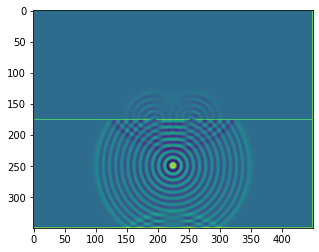
b = bb.wavebox(resolution = (350,450), size = (3.5,4.5))
# set initial state
#b.u = np.exp(-500*((b.x[0][:, None] - 1.5)**2 + b.x[1][None,:]**2))
#b.potential = lambda
def source(t):
return 20*np.exp(-500*((b.x[0][:, None] - 1.5)**2 + b.x[1][None,:]**2))*np.sin(25*t)
b.source = source
# set boundary conditions
b.set_neumann_boundary_conditions(boundaries_double_slit(b.resolution))
interference_pattern = np.zeros(b.resolution[1], dtype = float)
for i in range(20):
for j in range(80):
b.advance()
interference_pattern += b.u[1]**2
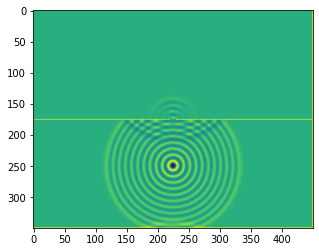
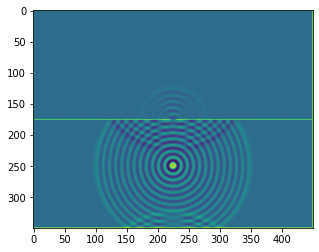
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(b.representation())
plt.show()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(interference_pattern)
plt.show()